Developing Cyanobacterial Quorum Sensing Toolkits - Toward Interspecies Coordination in Mixed Autotroph/Heterotroph Communities
Abstract
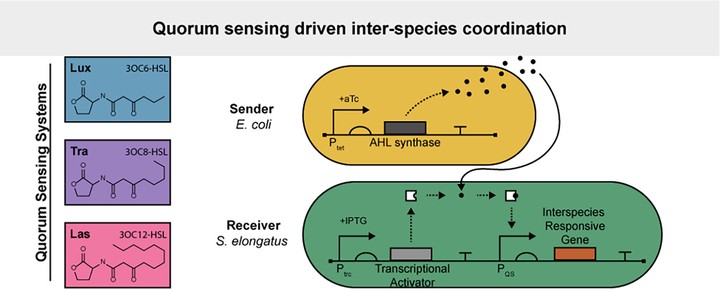
There has been substantial recent interest in the promise of sustainable, light-driven bioproduction using cyanobacteria, including developing efforts for microbial bioproduction using mixed autotroph/heterotroph communities, which could provide useful properties, such as division of metabolic labor. However, building stable mixed-species communities of sufficient productivity remains a challenge, partly due to the lack of strategies for synchronizing and coordinating biological activities across different species. To address this obstacle, we developed an inter-species communication system using quorum sensing (QS) modules derived from well-studied pathways in heterotrophic microbes. In the model cyanobacterium, Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942 (S. elongatus), we designed, integrated, and characterized genetic circuits that detect acyl-homoserine lactones (AHLs), diffusible signals utilized in many QS pathways. We showed that these receiver modules sense exogenously supplied AHL molecules and activate gene expression in a dose-dependent manner. We characterized these AHL receiver circuits in parallel with Escherichia coli W (E. coli W) to dissect species-specific properties, finding broad agreement, albeit with increased basal expression in S. elongatus. Our engineered “sender” E. coli strains accumulated biologically synthesized AHLs within the supernatant and activated receiver strains similarly to exogenous AHL activation. Our results will bolster the design of sophisticated genetic circuits in cyanobacterial/heterotroph consortia and the engineering of QS-like behaviors across cyanobacterial populations.